Application - Vaccination-induced antibody functionalities and protection
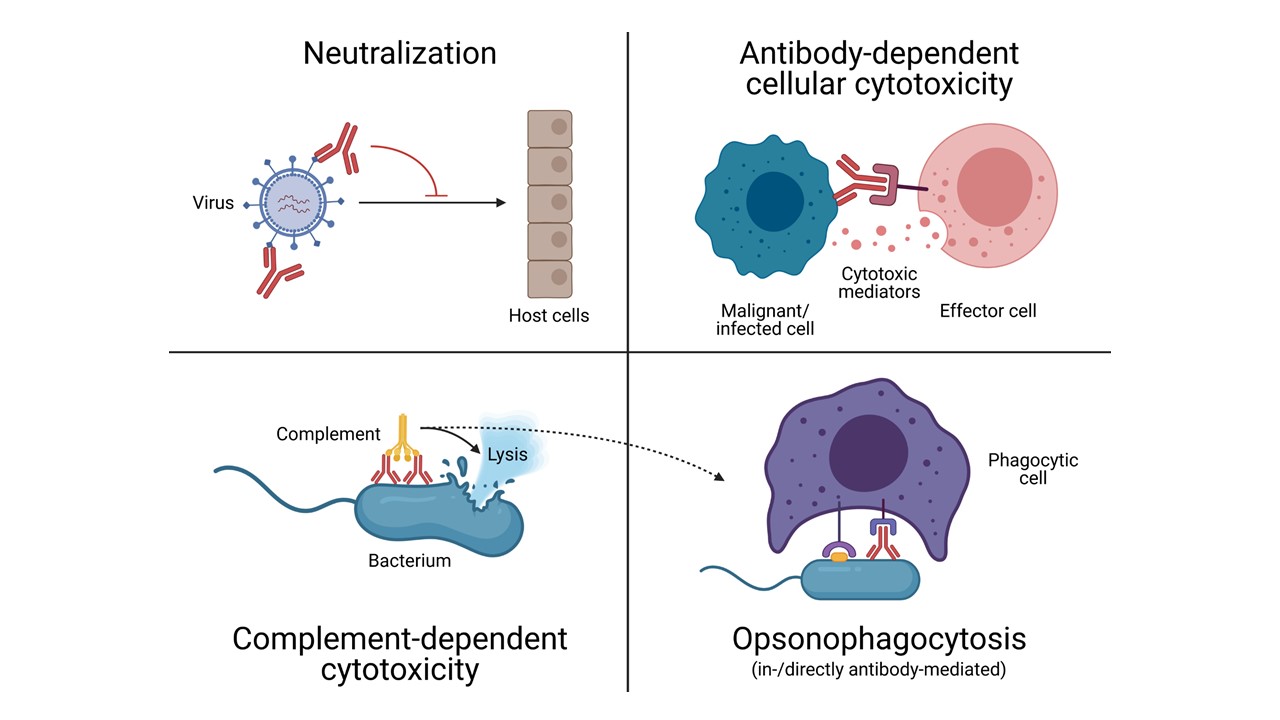
The adaptive immune system plays an important role in ensuring that vaccinations are successful and protect their recipient. This role is often performed by antibodies, which are able to bind the target and thereby reduce its negative effects on the host organism. However, binding is only the first step for the various effector functions that can be triggered by antibodies. These effector functions range from neutralization to activation of the complement system and accessory effector cells (see Figure). Not all of these functions can be triggered by any antibody that simply binds the target; many are related to its characteristics and the nature of the binding partner. It has been well described that different biological agents need to induce different immune responses within a species to be successfully encountered. This cannot only be true for the natural encountering of antigens, but also have an impact on the protection given by vaccines. We suggest therefore that depending on the nature of the threat (virus, bacteria, toxin or other) different functional repertoires are required. Thus, when evaluating new vaccine candidates, these possible functions have to be carefully monitored and quantified to adapt the vaccine candidate to generate the most beneficial response.
We develop and use a new, cutting-edge technology to shed light into these complex reactions, with the goal to firstly quantify, secondly understand, and lastly influence the immunological reaction upon vaccination. The objective of this project is not only to develop new analytical approaches to be able to quantitatively map antibody functions with individual cell resolution, but to use these data sets to understand the underlying selection mechanisms involved in their generation, evolution and transfer to memory of the antibody repertoires. Multiple variations of these data sets allow separating the influence of different vaccine components, dose and kinetics, as well as the cells from the immune system themselves. Such knowledge provides helpful insights for the development of new vaccine candidates and to better understand vaccine-mediated protection.
This project is a collaboration between various current, former and external members of the group - you can find the contact information of our current internal members below.
Contact
Funktion. Immunrepertoireanalyse
Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 1-5/10
8093
Zürich
Switzerland
Funktion. Immunrepertoireanalyse
Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 1-5/10
8093
Zürich
Switzerland
Funktion. Immunrepertoireanalyse
Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 1-5/10
8093
Zürich
Switzerland